Table of Contents
ToggleUser experience (UX) plays a crucial role in determining the success of a website or application. UX testing is the process of evaluating a product or service by observing real users interacting with it. UX testing aims to identify usability issues, uncover user needs and preferences, and ultimately improve the overall experience. This comprehensive guide will discuss the ten most effective UX testing methods that can help businesses optimize their digital products.
1. Surveys
Surveys are one of the simplest and most popular usability testing methods employed during a project’s early stages. They involve collecting user feedback through a series of questions, which can help identify existing pain points, user motivations, and preferences.
How and When to Use
Surveys are particularly useful when redesigning or redeveloping an existing website or application. By conducting online or email surveys, you can gather valuable insights from users while they interact with your product. This information can inform design decisions and ensure your updated product meets user expectations.
Considerations
- Ensure that survey questions are clear, concise, and relevant to your research objectives.
- Use both open-ended and closed-ended questions to gather a mix of quantitative and qualitative data.
- Keep the survey length reasonable to avoid respondent fatigue and encourage completion

. Card Sorting
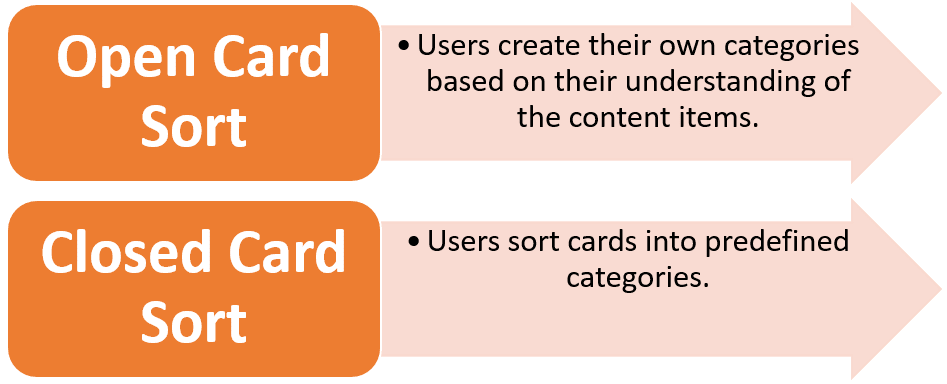
Card sorting is a UX testing method that involves users organizing content items or features into categories. This technique helps to evaluate the information architecture and navigation structure of a website or application, ensuring that users can quickly and easily find the information they need.
How and When to Use
Card sorting can be employed during the planning and strategy stage of a project. Participants are provided with a set of cards, each representing a piece of content or feature, and asked to group them according to their understanding. The resulting groupings can then be used to inform the design of your product’s information architecture and navigation.
Types of Card Sorting
Considerations
- Test with a diverse group of users to account for varying mental models and perspectives.
- Analyze the results to identify common patterns and outliers, which can inform the final information architecture.
3. Tree Testing
Tree testing, also known as reverse card sorting, is a UX testing method that evaluates the effectiveness of a product’s information architecture. It involves providing users with a hierarchical structure of your product’s content and asking them to locate specific items within the structure.
How and When to Use
Tree testing is typically conducted after card sorting or during the design and build stage of a project. By analyzing user performance in locating items, you can identify potential navigation issues and make improvements to your product’s information architecture.
Considerations
- Ensure that the hierarchical structure used in the test accurately represents your product’s content.
- Test with a diverse group of users to account for varying levels of familiarity with the content and domain.
4. First Click Testing
First, click testing is a UX testing method that examines user behavior during the initial interaction with a website or application. Users are asked to find specific information or complete a task, and their first click is recorded and analyzed.
How and When to Use
First-click testing is best suited for interactive wireframes, home pages, or landing page concepts. By analyzing users’ initial clicks, you can identify potential issues with the layout, content hierarchy, or call-to-action elements and make necessary adjustments.
Considerations
- Ensure that test tasks are clear and representative of real-world usage scenarios.
- Analyze the results to identify patterns in user behavior and areas for improvement.
5. Five-Second Test
The five-second test is a UX testing method that focuses on users’ first impressions of a design. Participants are shown a design, such as a webpage or an app screen, for just five seconds and then asked a single question about their impression.
How and When to Use
Five-second testing is ideal for evaluating design concepts and assessing how quickly a design can convey its intended message. This method can be used during the design stage of a project to ensure that your product effectively communicates its purpose and appeals to its target audience.
Considerations
- Craft the test question carefully to ensure it aligns with your research objectives and provides meaningful insights.
- Test with a diverse group of users to account for varying perspectives and preferences.
6. Heat Maps
Heat maps are a powerful UX testing tool that visually represents user interactions on a website or application. By tracking mouse movements, clicks, and other interactions, heat maps can provide valuable insights into user behavior and identify potential usability issues.
How and When to Use
Heat maps can be employed during the design and build stage of a project, as well as for ongoing analysis of user behavior. They can help identify areas of high user engagement, as well as areas where users may be experiencing confusion or frustration.
Considerations
- Use heat maps in conjunction with other UX testing methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of user behavior.
- Analyze heat map data to identify trends and inform design improvements.
7. Keystroke Level Analysis
The keystroke-level analysis is a UX testing method that measures the efficiency of a user interface by counting the number of clicks, keystrokes, and other actions required to complete a task.
How and When to Use
This method is best suited for in-house testing by development teams, as it provides an objective benchmark for evaluating the efficiency of a user interface. By identifying tasks that take too long or require too many actions, you can streamline your product’s interface and improve overall usability.
Considerations
- Use real-world user scenarios to ensure that the tasks being tested are representative of actual user experiences.
- Compare keystroke-level analysis results with other UX testing methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of your product’s usability.
8. A/B Testing
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a UX testing method that compares two versions of a website or application to determine which performs better. Users are randomly assigned to one of the two versions, and their interactions are tracked and analyzed to identify the most effective design.

How and When to Use
A/B testing is often used for optimizing landing pages and marketing campaigns, but it can also be employed during the design and build stage of a project to test different design elements or features. By identifying the most effective version, you can ensure that your product meets user needs and preferences.
Considerations
- Limit the number of changes between the two versions to one significant element to ensure that the test results are reliable and actionable.
- Test with a large enough sample size to ensure statistically significant results.
9. Guerrilla Testing
Guerrilla testing is a quick and cost-effective UX testing method that involves recruiting participants at random from public places, such as coffee shops or malls, to complete usability tests in exchange for a small incentive.
How and When to Use
Guerrilla testing can be used during any project stage, but it is particularly useful for testing new features or updates before they are released to a wider audience. Gathering immediate user feedback lets you quickly identify and address any usability issues before they impact more users.
Considerations
- Ensure that test tasks are clear, concise, and representative of real-world usage scenarios.
- Be prepared to adapt and iterate on your product based on the feedback received from guerrilla testing.
10. Lab Testing
Lab testing is an in-depth UX testing method that involves observing users as they complete tasks in a controlled environment, often with a moderator present to guide and ask questions.
How and When to Use
Lab testing is ideal for evaluating the overall user experience of a fully-built website or application, either before or after its launch. By observing users as they interact with your product, you can gain valuable insights into their needs, preferences, and pain points, which can inform future improvements.
Considerations
- Ensure that test tasks are representative of real-world user scenarios and cover all aspects of your product’s user experience.
- Analyze the results of lab testing in conjunction with other UX testing methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of your product’s usability.
Conclusion
UX testing is essential to ensure that your website or application meets user needs and provides a seamless, enjoyable experience. By employing a combination of the ten effective UX testing methods discussed in this guide, you can optimize your digital products and achieve optimal results. You can benefit from these methods by availing top-quality UI/UX design & testing services. Remember to select the appropriate UX testing methods based on your project’s stage and goals, and always be prepared to adapt and iterate based on user feedback.