Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Cloud Computing and Cloud Service Models
The evolution of technology has heralded a paradigm shift in the way businesses operate. Cloud computing, a revolutionary concept, has emerged as the bedrock of modern business infrastructure. This article embarks on a comprehensive exploration of three pivotal cloud service models: Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). These models, each possessing unique attributes, have carved a niche in the digital arena, driving operational efficiency, innovation, and scalability.
Defining Cloud Computing and its Evolution
Cloud computing represents an evolutionary leap from traditional IT practices. The concept revolves around the virtualization of resources, enabling the transformation of hardware into flexible digital assets. The transition from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud is emblematic of the paradigm shift taking place in the IT landscape, rendering physical boundaries obsolete.
Importance of Cloud Service Models in Modern Business
The dynamic nature of modern business necessitates agility and flexibility. Cloud service models, SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS, embody the essence of adaptability. By embracing these models, businesses can effortlessly tailor their operations to meet fluctuating demands, effectively sidestepping bottlenecks and unlocking growth avenues.
Overview of SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS as Integral Components
At the core of contemporary IT architecture lie the foundational pillars of SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS. These cloud service models, akin to building blocks, cater to distinct business needs, redefining the way enterprises function.
Understanding SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS Definition and Core Characteristics
Software as a Service (SaaS) serves as a virtual conduit to software accessibility. Embracing SaaS, users can access applications and tools through the internet, circumventing the need for on-site installation. This model is characterized by its on-demand accessibility, multi-tenancy architecture, and automated updates—a testament to its user-centric design.
-
Benefits of SaaS Adoption for Businesses
The strategic integration of SaaS into business operations ushers in a multitude of benefits. Notably, it slashes IT overheads and operational costs, providing a cost-efficient alternative to traditional models. The rapid deployment offered by SaaS expedites time-to-market, ensuring businesses stay ahead of the curve. Moreover, the scalability and accessibility quotient make SaaS a stalwart in modern business landscapes.
-
Exploring Common SaaS Applications Across Industries
The ubiquitous nature of SaaS finds application across diverse sectors. It underpins Customer Relationship Management (CRM), propels Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and enhances collaboration through productivity suites. These applications exemplify SaaS’s role in streamlining operations, enhancing customer experiences, and driving business growth.
-
Considerations for Choosing SaaS Solutions
When embarking on the SaaS journey, prudent considerations come to the forefront. Data security emerges as a paramount concern, warranting rigorous scrutiny of encryption protocols and access controls. Seamless integration with existing systems is pivotal, ensuring continuity without disrupting established workflows. Vendor reputation and support form the backbone of a successful SaaS partnership, contributing to a cohesive business ecosystem.
Delving into IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS Defined and Key Attributes
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) heralds a new era of digital infrastructure provisioning. This model grants access to virtualized computing resources, spanning network components and storage solutions. The pay-as-you-go model further amplifies its appeal, allowing businesses to scale resources in alignment with evolving requirements.
-
Advantages of IaaS Implementation for Enterprises
The allure of IaaS lies in its potential to augment enterprise capabilities. By facilitating flexible resource allocation, IaaS empowers businesses to match resources to real-time demands, optimizing operational efficiency. Furthermore, the inherent disaster recovery capabilities and testing environments minimize downtime risks, ensuring uninterrupted operations even in the face of unforeseen challenges.
-
Use Cases for IaaS in Different Scenarios
The versatility of IaaS surfaces in various operational scenarios. Hosting web applications and websites thrive on the scalable foundation of IaaS. Additionally, IaaS is pivotal for processing vast volumes of data through Big Data analytics and supporting high-performance computing clusters. These applications epitomize the pivotal role of IaaS in powering modern enterprises.
-
Factors to Consider When Opting for IaaS
The selection of an appropriate IaaS provider mandates a holistic evaluation. Performance requirements demand meticulous attention, with latency considerations taking precedence. Data management and compliance emerge as critical considerations, safeguarding data integrity and adherence to regulatory standards. Network security and real-time monitoring round off the list of crucial IaaS selection criteria.
Exploring PaaS (Platform as a Service)

PaaS Overview and Notable Features
Platform as a Service (PaaS) stands as a testament to streamlined business app development. Equipped with middleware and development tools, PaaS offers a simplified pathway for application deployment. This model’s hallmark lies in its emphasis on coding and innovation, enabling developers to channel their efforts into creativity.
-
Pros of Embracing PaaS Solutions in Software Development
PaaS orchestrates a symphony of benefits for software development endeavors. Its role in expediting development cycles, fostering collaboration among development teams, and integrating DevOps practices cannot be overstated. The integrated nature of PaaS solutions streamlines workflows, fostering efficiency and productivity.
-
Instances Where PaaS Excels for Businesses
The domains in which PaaS excels are diverse and impactful. It shines as a beacon of innovation for startups and rapid prototyping. PaaS also navigates the complexities of Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD), expediting application deployment. Moreover, the sphere of mobile app development bears witness to PaaS’s transformative potential.
-
Critical Factors to Evaluate in PaaS Selection
PaaS selection necessitates a discerning evaluation of multiple facets. Language and framework support define the development landscape, enabling businesses to leverage their preferred tools. Scalability considerations are paramount, ensuring the platform can evolve in tandem with business growth. Additionally, strategies to mitigate vendor lock-in effects assume significance, safeguarding flexibility and long-term compatibility.
Comparative Analysis of SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS
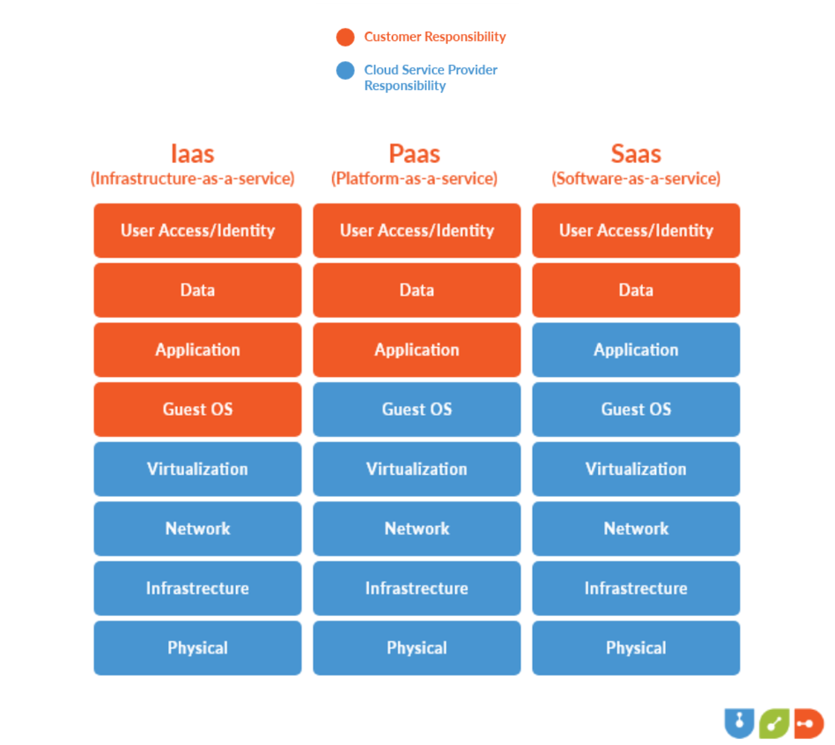
Differentiating Between Service Models
Distinct characteristics set SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS apart. The abstraction of service levels, distribution of responsibilities through the shared responsibility model, and the extent of user experience customization serve as key markers of differentiation.
-
Assessing Costs and Budget Implications Across Models
Financial considerations play a pivotal role in cloud service model selection. The subscription-based pricing model of SaaS, the pay-per-usage structure of IaaS, and the nuanced pricing complexity of PaaS each warrant careful assessment, ensuring alignment with budgetary constraints.
-
Scalability and Resource Allocation Variations
Scalability emerges as a cornerstone of cloud services. SaaS thrives on elastic scaling, adapting to fluctuating user demands. IaaS fosters infrastructure scalability, empowering businesses to match resources to requirements. PaaS, in turn, boasts horizontal scaling and auto-scaling capabilities, striking a balance between resource allocation and efficiency.
-
Integration and Customization Considerations
Integration and customization serve as compass points in cloud adoption. SaaS grapples with API integration challenges, requiring seamless interfacing with existing systems. IaaS entails infrastructure integration, with the onus of harmonizing disparate components. PaaS navigates the terrain of custom code and third-party service integration, fostering adaptability and innovation.
Factors Influencing Cloud Service Model Selection
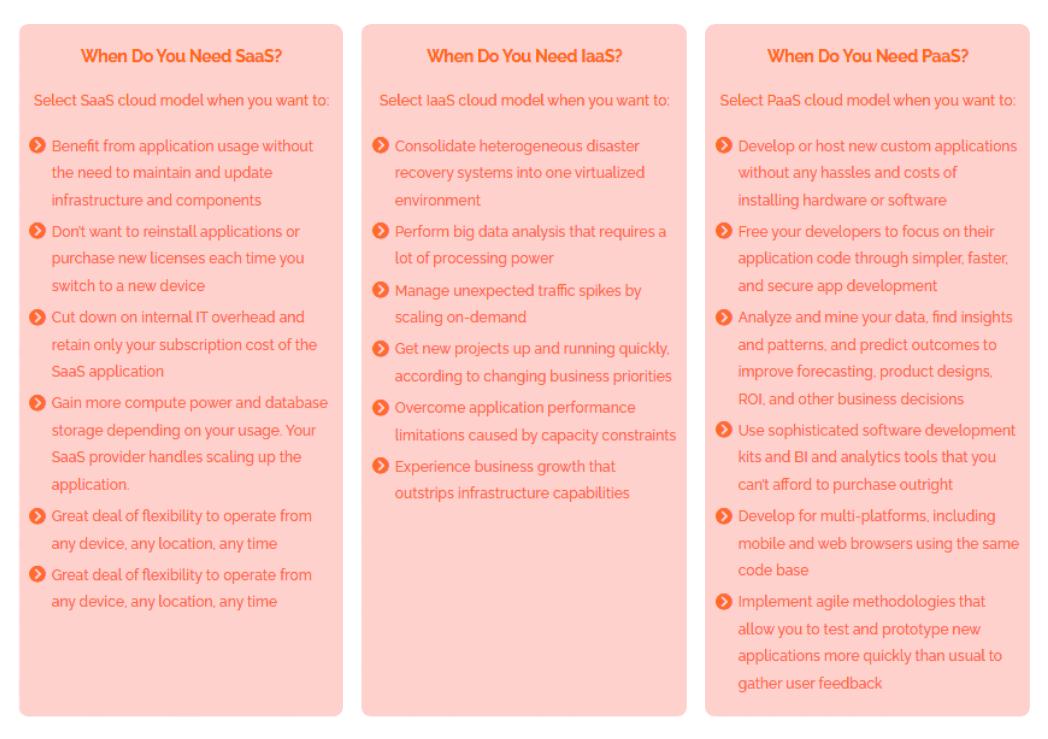
Business Type and Goals as Decision Drivers
The selection of a cloud service model hinges on business type and aspirations. Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) gravitate towards SaaS for cost-effectiveness. Enterprises, on the other hand, harness IaaS for complex workloads. Startups find solace in PaaS, capitalizing on its innovation-fueling capabilities.
Technical Expertise and Resource Availability
Technical prowess and resource availability direct cloud service model selection. The skill set required for SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS warrants careful assessment. Moreover, the decision between in-house resources and outsourcing shapes the direction of cloud adoption. The learning curve and training considerations further influence the alignment of technical proficiency with the chosen model.
Security and Compliance Requirements
Security stands at the forefront of cloud adoption deliberations. Cloud service models differ in their data security mechanisms, prompting businesses to tailor their selection based on the sensitivity of their data. Regulatory compliance and data governance further underscore the selection process, with adherence to GDPR, HIPAA, and other industry-specific standards assuming paramount importance. The shared responsibility model elucidates the distribution of security responsibilities, necessitating adherence to best practices and user actions.
Performance and Scaling Needs for Business Growth
Business growth is intrinsically linked to performance and scalability. Anticipating performance bottlenecks and planning for peak loads are pivotal to ensure uninterrupted operations during periods of heightened demand. Seamlessly scaling resources without downtime reinforces business continuity and reinforces customer experiences.
Real-world Case Studies of Cloud Service Model Implementation
SaaS Implementation Success Story: Salesforce CRM
Salesforce CRM stands as an embodiment of SaaS’s transformative potential. Its integration revolutionized customer relationship management, cascading into elevated sales figures and enhanced customer service. This success story exemplifies the seamless scalability, accessibility, and collaborative potential of SaaS.
IaaS Adoption in a Business Context: Netflix
Netflix, a global entertainment juggernaut, provides a compelling case for IaaS adoption. Leveraging cloud infrastructure, Netflix handles colossal workloads, particularly during peak usage periods. The flexibility and scalability of IaaS ensure uninterrupted streaming experiences, driving customer satisfaction.
PaaS Integration for Streamlined Development: Airbnb
Airbnb’s journey toward success has been marked by PaaS integration. PaaS expedites application deployment and updates, enabling Airbnb to roll out features rapidly and foster innovation. The streamlined development process is instrumental in meeting customer expectations and maintaining a competitive edge.
Pros and Cons of Each Cloud Service Model
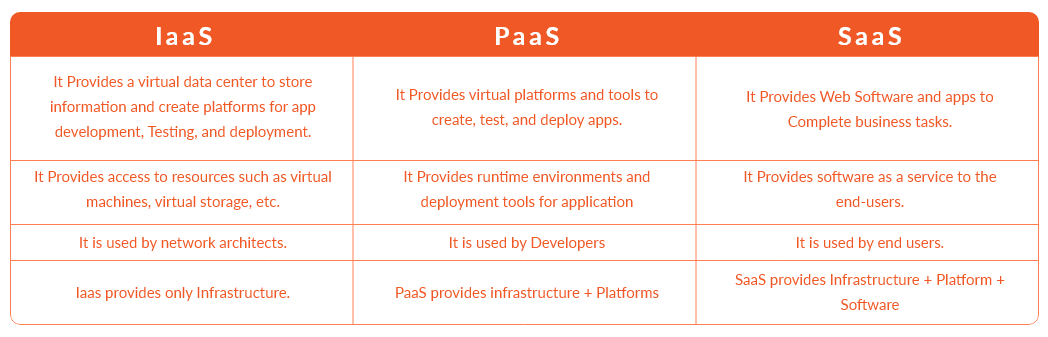
SaaS: Advantages and Limitations for Businesses
SaaS embodies a plethora of advantages. Reduced maintenance efforts and costs liberate businesses from the shackles of upkeep. However, the trade-off lies in the realm of customization and control, as SaaS solutions may lack the tailored functionality required by certain enterprises. The interplay of data security and compliance introduces a layer of complexity that necessitates careful consideration.
IaaS: Benefits and Drawbacks in Infrastructure Management
IaaS dons the mantle of flexibility and scalability, providing businesses with virtualized resources that adapt to dynamic demands. However, the onus of server and network management rests on the business, mandating technical expertise and administrative efforts. The duality of reduced infrastructure costs and the need for dedicated resources adds nuance to the IaaS landscape.
PaaS: Pros and Challenges in Development Environments
The realm of PaaS resonates with accelerated development cycles and seamless deployment processes. The inherent collaboration among development teams and integrated DevOps practices propel innovation. However, constraints on infrastructure customization and vendor lock-in vulnerabilities underscore the need for strategic planning when embracing PaaS.
Key Considerations for Migration to Cloud Services
Planning and Preparation Phase for Migration
The migration journey commences with meticulous planning and preparation. Evaluating the existing IT landscape, defining a migration strategy, and identifying potential roadblocks lay the foundation for a seamless transition.
Data Migration and Transfer Strategies
Data forms the lifeblood of modern enterprises, making data migration and transfer strategies indispensable. Meticulous data mapping and structured migration plans preserve data integrity, while minimizing downtime assumes critical importance. Validation and post-migration monitoring validate the success of the migration process, instilling confidence in the newly adopted cloud environment.
Ensuring Minimal Disruption to Operations
Transitioning to the cloud should be characterized by minimal operational disruption. Testing and simulating the migration process proactively address challenges, enabling organizations to anticipate and circumvent potential roadblocks. Effective communication and collaboration with stakeholders during the migration process foster transparency and engender trust. Post-migration monitoring and support mechanisms ensure that the newly embraced cloud services operate seamlessly.
Addressing Security and Privacy Concerns in Cloud Adoption
Security Measures Across Different Service Models
Security forms the bedrock of cloud adoption. SaaS leverages encryption and access controls to fortify data security. IaaS introduces network segmentation and firewalls to safeguard infrastructure, while PaaS adopts containerization and application security mechanisms to ensure robust security.
Data Privacy Regulations and Compliance
Data privacy and regulatory compliance constitute non-negotiable aspects of cloud adoption. Regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA dictate data residency, cross-border transfer, and data ownership protocols. Negotiating vendor agreements that adhere to regulatory standards safeguards data privacy and instills confidence in cloud adoption.
Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Security
The shared responsibility model demarcates security responsibilities between cloud service providers and customers. Users must adopt security best practices and adhere to policies to bolster the security of their cloud environment. Fostering a culture of security awareness among users forms an integral component of the shared responsibility framework.
Future Trends in Cloud Service Models and Computing
Evolving Landscape of SaaS: AI and Automation
The trajectory of SaaS is guided by the integration of AI and automation. AI-driven personalization and insights usher in a new era of customer experiences, while predictive maintenance and decision support algorithms elevate operational efficiency.
IaaS Innovations on the Horizon: Edge Computing
The horizons of IaaS expand with the advent of edge computing. This paradigm empowers businesses to process data closer to its source, minimizing latency for latency-sensitive applications. The convergence of IoT and edge analytics marks a pivotal chapter in IaaS evolution.
PaaS Advancements and Emerging Technologies
PaaS continues its trajectory of innovation with serverless computing and event-driven architectures. These technologies eliminate the need for provisioning and scaling of infrastructure, while Kubernetes and container orchestration enhance application development and deployment efficiency.
Selecting the Right Cloud Service Model for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate cloud service model entails a systematic decision-making process. Identifying business goals and requirements acts as the foundational step, enabling alignment with the intended outcomes. Evaluating technical considerations, including IT skillset requirements and resource availability, paves the way for an informed choice. Weighing the pros and cons of each model in light of business objectives ensures a tailored decision.
The selection of a cloud service model must be a reflection of business aspirations. Aligning the chosen model with growth plans, considering budget constraints, and evaluating resource availability reinforces the strategic value of cloud adoption. Long-term scalability and flexibility considerations lend foresight to the decision-making process.
Case-specific Analysis: Which Service Model for Which Scenario
Small Business with Limited Resources
Small businesses with constrained resources find solace in cost-efficient SaaS solutions. SaaS affords startups the means to streamline operations without overwhelming overheads. IaaS offers scalability that matches the pace of controlled growth, while PaaS facilitates rapid prototyping and innovation, empowering small businesses to stay agile.
Large Enterprise with Complex Infrastructure
Large enterprises, equipped with intricate infrastructure, find their match in SaaS for collaboration and productivity enhancements. IaaS emerges as a cornerstone for managing hybrid infrastructure, fostering agility and scalability. PaaS’s capacity to accelerate innovation and development resonates with large enterprises seeking to maintain a competitive edge.
Software Development and Deployment Project
Software development and deployment projects gain immense value from cloud service models. SaaS tools streamline project management and collaboration, facilitating efficient development. IaaS provides the infrastructure needed for development and testing environments, while PaaS fosters a culture of continuous integration and deployment, enabling swift application rollout.
Industry-specific Applications of Cloud Service Models
Healthcare and Medical Services
Healthcare finds an ally in SaaS for Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems. IaaS serves as the bedrock for medical imaging and data storage, while PaaS catalyzes the healthcare software development. These applications underscore the adaptability and scalability of cloud service models in the healthcare domain.
E-commerce and Retail
The retail landscape embraces SaaS-based online storefronts and payment solutions, catering to evolving customer preferences. IaaS plays a pivotal role in scaling e-commerce infrastructure, ensuring seamless customer experiences. PaaS drives customization in shopping experiences, enabling retailers to tailor interactions to individual needs.
Finance and Fintech
Finance and Fintech sectors leverage SaaS for accounting and financial management software, ensuring compliance and accuracy. IaaS secures financial transactions through its robust infrastructure, while PaaS catalyzes the development of financial analytics tools, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Best Practices for Maximizing Cloud Service Model Benefits
Effective Utilization of SaaS Resources
Maximizing the benefits of SaaS necessitates continuous assessment of software usage and needs. Streamlining user training and adoption, coupled with the utilization of automation and workflows, optimize resource utilization.
Optimization Strategies for IaaS Performance
IaaS performance optimization entails monitoring resource utilization and performance metrics. Implementing load balancing and scaling policies, along with efficient virtual machine and networking management, enhances infrastructure performance.
Enhancing Development Workflow with PaaS
Enhancing development workflows through PaaS requires leveraging built-in development tools and APIs. Embracing containerization and microservices, while continuously integrating and deploying applications, fosters efficiency in the development process.
Addressing Common Misconceptions about Cloud Services
Myth-busting SaaS Misunderstandings
Dispelling myths around SaaS involves addressing data security and ownership concerns. Clarifying the myths surrounding performance and offline access facilitates informed decision-making.
Clarifying IaaS Perceptions and Realities
Addressing misconceptions related to server management and resource allocation is essential. Shedding light on the balance between scalability and infrastructure costs guides accurate IaaS understanding.
PaaS Misconceptions Unveiled
Unveiling PaaS misconceptions involves clarifying limitations related to development constraints and vendor lock-in. Addressing concerns about security and data control fosters transparency.
Tips for Successful Implementation and Adoption
Smooth Onboarding Process for Cloud Services
A successful onboarding process hinges on communicating benefits to stakeholders effectively. Training end users and administrators, coupled with addressing initial challenges transparently, ensures a seamless transition.
Training and Skill Development for Cloud Management
Ensuring effective cloud management demands upskilling IT teams for the intricacies of cloud operation. Offering ongoing training and certification opportunities fosters a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
Change Management and Employee Engagement Strategies
Navigating change management requires managing resistance and involving employees in decision-making. Recognizing successes and fostering employee engagement fortify the transition to cloud services.
Realizing ROI (Return on Investment) with Cloud Services
- Measuring SaaS ROI entails calculating cost savings, assessing business impact, and quantifying user satisfaction. The culmination of these metrics provides a comprehensive view of SaaS’s tangible and intangible returns.
- IaaS investment returns encompass reduced infrastructure costs and minimized downtime. Analyzing downtime reduction and business continuity, while considering long-term scalability and competitive advantages, paints a holistic picture of IaaS’s ROI.
- Calculating PaaS benefits translates to evaluating time-to-market acceleration, reduced development costs, and improved application quality. PaaS’s role in fostering innovation and enhancing user experience completes the ROI equation.
Summary: Making the Right Choice for Your Cloud Needs
SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS present distinct avenues for modern businesses to embark on a journey of digital transformation. Understanding the unique attributes of each service model empowers businesses to make informed choices that align with their goals and aspirations.