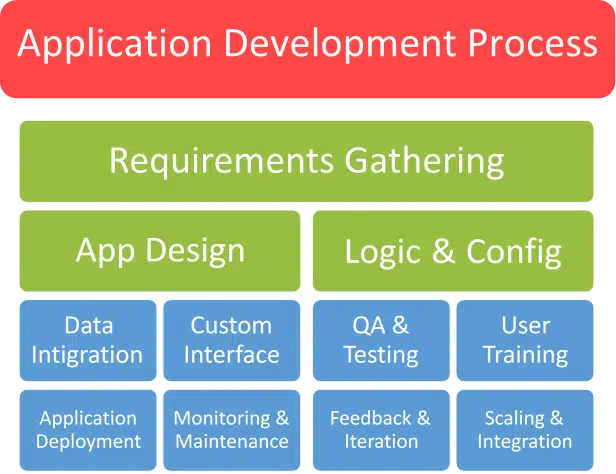
Inspirations can emerge from a variety of sources, irrespective of an individual’s background, culture, and education. High development rates and per-hour wage of a developer can inspire anyone to become a programmer or, simply, a coder. However, becoming a coder is a matter of ambition rather than capability. Anyone can learn to code and excel if they have a passion for it.
Boarding on learning to code often raises questions of diverse nature and domains, confusing many people. Such include the relationship between coding and math, the responsibilities of programmers, and the essential requirements to flourish professionally. This blog addresses such queries and offers insights into becoming a proficient programmer, regardless of your position.

A. Does Coding Involve Math? Do You Need Math for Coding?
One common misconception is that coding requires advanced mathematical skills. While certain areas of programming, such as algorithms and data science, involve math, many aspects of coding do not necessitate extensive mathematical knowledge. Basic math skills are beneficial, but creative problem-solving and logical thinking are equally crucial.
The relationship between coding and mathematics is a common inquiry among most aspiring programmers. Let’s delve deeper into these questions: Does coding involve math? Or Do you need math for coding?
1) Debunking the Myth
One common misconception is that proficiency in advanced mathematics is a prerequisite for coding. Certain aspects of programming, such as complex algorithms or data science, may indeed involve mathematical concepts. However, the broader landscape of coding accommodates a diverse set of skills. The fundamental principles of programming emphasize logical reasoning, problem-solving, and algorithmic thinking. It includes some more aspects that don’t necessarily rely on intricate mathematical formulas.
2) Basic Math Skills vs. Advanced Mathematics
It’s essential to distinguish between basic math skills and advanced mathematics in the context of coding. Basic arithmetic, algebraic understanding, and logical reasoning are valuable assets in coding. They enable developers to make informed decisions, create efficient algorithms, and troubleshoot code effectively. However, an in-depth understanding of calculus or higher-level mathematics is often not a strict requirement for many coding tasks.
3) Focus on Problem-Solving
Coding fundamentally revolves around problem-solving. Developers analyze challenges, break them down into manageable components, and devise solutions through code. This problem-solving approach draws more from critical thinking and logic than from intricate mathematical calculations. In essence, the ability to think logically and approach problems systematically is a cornerstone of successful coding endeavors.
4) Specialized Areas, Algorithms, and Data Science
While foundational coding may not heavily rely on advanced mathematics, certain specialized areas within programming, such as designing complex algorithms or engaging in data science, may require a more profound understanding of mathematical concepts. In these cases, familiarity with mathematical principles can indeed enhance a developer’s ability to create efficient algorithms, analyze data patterns, and optimize code performance.
The relationship between coding and math is complex. While basic math skills are often sufficient for much of coding, advanced mathematical knowledge becomes more prominent in specialized areas. Aspiring programmers should focus on improving their problem-solving skills, logical reasoning, and algorithmic thinking. They must recognize that the diverse field of coding accommodates a range of skill sets. Ultimately, the decision to learn mathematics depends on individual goals and the specific areas of coding one wishes to explore.
B. What Does a Computer Programmer Do on a Daily Basis?
Computer programmers engage in diverse tasks daily. They write, test, and debug code, collaborate with team members, and participate in project planning. Daily responsibilities may also include troubleshooting issues, updating existing code, and staying abreast of industry trends. Effective communication and teamwork are integral to a programmer’s daily routine.
Computer programmers engage in diverse tasks on a daily basis, contributing to the dynamic and shape-shifting field of programming. Let’s probe into their daily responsibilities and explore the essential requirements to thrive in this multifaceted role.
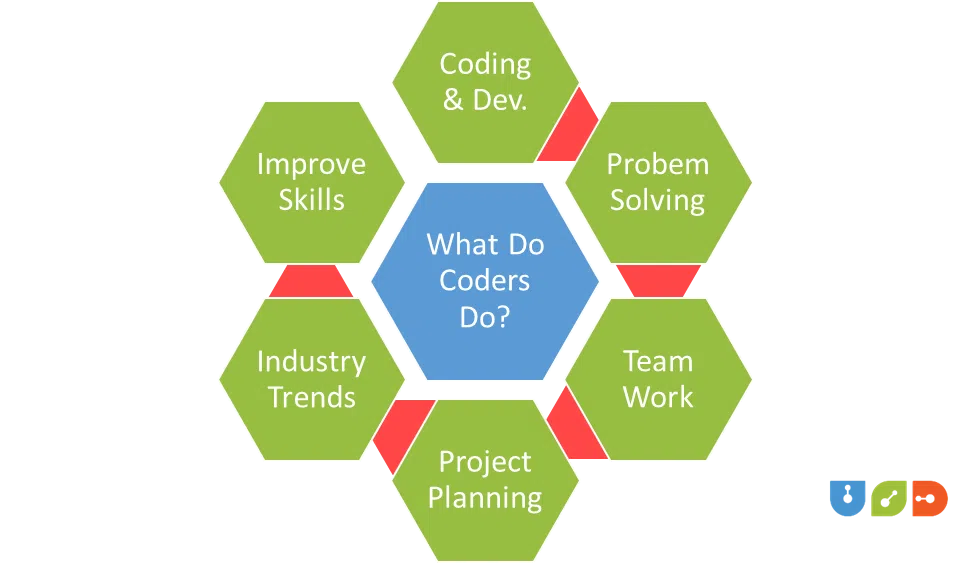
1) Coding and Development
The core of a programmer’s daily activities revolves around coding and development. They write, test, and debug code to create software applications. It comprises collaborating with other team members to ensure the code aligns with project goals and adheres to coding standards.
2) Problem-Solving
Every day presents new challenges, and computer programmers are adept problem-solvers. They tackle issues, troubleshoot bugs, and optimize existing code for efficiency. It requires a keen analytical mindset and the ability to think critically to identify and implement effective solutions.
3) Collaboration and Teamwork
Programming is rarely a solitary endeavor, even when it is a lone journey. Programmers often collaborate with other team members, including fellow developers, designers, and project managers. Effective communication and teamwork are crucial as programmers work together to achieve project milestones and deliver high-quality software.
4) Project Planning and Coordination
In addition to writing code, programmers participate in project planning and coordination. It involves understanding project requirements, estimating timelines, and contributing to the overall project strategy. Effective project management skills enhance a programmer’s ability to meet deadlines and deliver successful outcomes.
5) Staying Abreast of Industry Trends
The tech industry evolves rapidly, and programmers need to stay informed about the latest trends, tools, and technologies. Daily tasks may include reading industry news, following tech blogs, and participating in online coding communities to remain up-to-date with advancements that could impact their work.
C. Requirements to Be a Programmer
To thrive as a programmer, a foundational understanding of programming languages like Python, Java, or JavaScript is essential. A degree in computer science or a related field is valuable but not mandatory. Strong analytical skills, attention to detail, and a passion for problem-solving are key attributes that employers seek in programmers.
1) Building the Foundation for Success
To thrive as a programmer, a holistic approach to skill development and education is key. Let’s delve into the essential requirements that pave the way for a successful career in programming.
a) Foundational Knowledge in Programming Languages
Developing a strong foundation in programming languages is paramount. Proficiency in versatile languages like Python, Java, or JavaScript provides the versatility needed to adapt to various coding challenges. Numerous online platforms, such as Codecademy or freeCodeCamp, offer interactive learning environments for mastering these languages.
b) Educational Background
While a degree in computer science or a related field is valuable, it’s not the sole path to success. Many successful programmers have honed their skills through self-directed learning and practical experience. Formal education can provide a structured understanding of computer science fundamentals, algorithms, and data structures, offering a comprehensive knowledge base.
c) Analytical Skills and Attention to Detail
The ability to analyze problems critically and pay meticulous attention to detail distinguishes a proficient programmer. Successful coding often involves breaking down complex issues into manageable parts, requiring a keen analytical mindset and an eye for precision.
d) Passion for Problem-Solving
In the dynamic realm of programming, problem-solving is at the core. A genuine passion for tackling challenges head-on and finding creative solutions is a driving force. Enthusiasm for overcoming obstacles ensures a proactive and resilient approach to coding tasks.
e) Continuous Learning Mindset
The tech landscape evolves rapidly, demanding a commitment to continuous learning. Stay updated on emerging technologies, industry trends, and advancements in programming methodologies. Engage with coding communities, attend conferences, and participate in online forums to remain at the forefront of the ever-changing tech ecosystem.
f) Effective Communication and Teamwork
Programming is rarely a solitary endeavor. Effective communication skills are crucial for collaborating with team members, articulating ideas, and understanding project requirements. A programmer’s ability to work seamlessly within a team contributes to the success of a project.
g) Practical Experience
Gaining hands-on experience through internships, coding projects, or open-source contributions is invaluable. Practical exposure allows aspiring programmers to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, enhancing problem-solving skills and building a robust portfolio of projects.
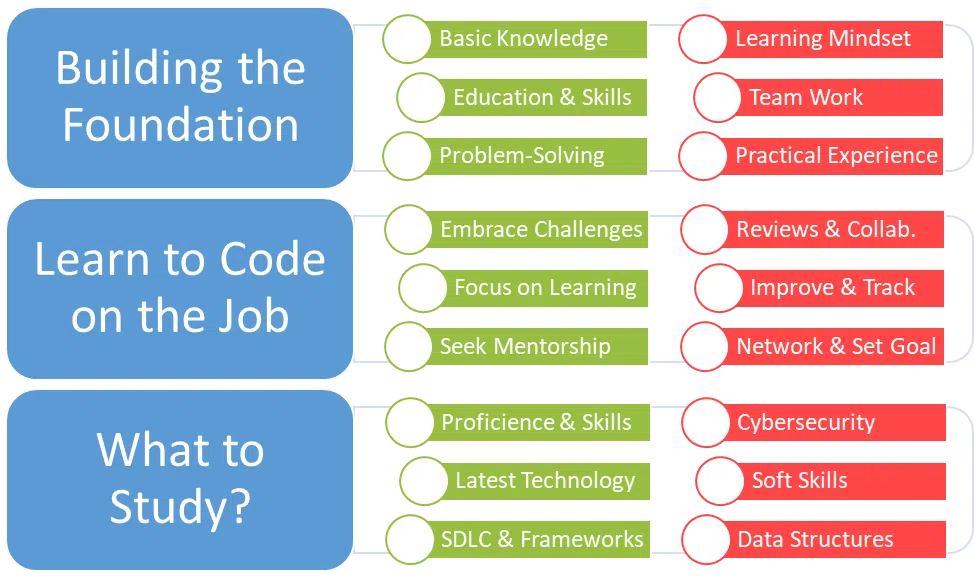
The requirements to be a successful programmer extend beyond technical proficiency. A combination of foundational knowledge, analytical skills, continuous learning, and practical experience forms the bedrock of a thriving programming career. Embrace these requirements as building blocks on your coding journey, and you’ll be well-prepared to navigate the dynamic and exciting world of programming.
2) Learn to Code on the Job to Become a Pro
Learning to code on the job is a viable path to becoming a proficient programmer. Practical experience through internships, coding boot camps, or entry-level positions accelerates learning. Embrace challenges, seek mentorship, and continuously refine your coding skills to become a well-rounded and effective programmer. Learning on the job is a dynamic and immersive experience that can significantly contribute to becoming a proficient programmer. Here are essential strategies to harness the full potential of on-the-job learning:
a) Embrace Challenges and Seek Diverse Projects
One of the most effective ways to enhance your coding skills on the job is to seek out challenges actively. Voluntarily participate in any projects that expose you to the different aspects of coding. Whether it’s front-end development, back-end architecture, or database management, it broadens your skill set and makes you a seasoned programmer.
b) Cultivate a Learning Mindset
Approach every task with a learning mindset. Acknowledge that every project, big or small, offers an opportunity to acquire new skills and insights. Be open to feedback, learn from mistakes, and continuously seek ways to optimize your code. A growth-oriented mindset is key to evolving into a successful programmer.
c) Leverage Mentorship Opportunities
If your workplace offers mentorship programs or if there are experienced programmers on your team, take advantage of these resources. Learning from seasoned professionals provides valuable insights, tips, and best practices. Establishing a mentor-mentee relationship can accelerate your learning curve and expose you to industry wisdom.
d) Actively Participate in Code Reviews
Code reviews are invaluable learning opportunities. Actively participate in and contribute to code reviews, whether it’s reviewing your work or providing feedback to others. Engaging in this collaborative process exposes you to different coding styles, best practices, and potential pitfalls. It’s a continuous learning exchange that fosters improvement.
e) Collaborate with Cross-Functional Teams
Programming is rarely a solitary endeavor. Working with cross-functional teams exposes you to different perspectives and skills. Engage with designers, project managers, and quality assurance professionals. Understanding the holistic development process enhances your ability to write code that aligns with broader project goals.
f) Continuous Skill Refinement
On-the-job learning doesn’t end with the completion of a project. Actively seek opportunities for continuous skill refinement. Stay updated on the latest tools, frameworks, and industry trends. Attend workshops, webinars, and conferences to stay connected with the developer community and gain insights into emerging technologies.
g) Document Your Learning Journey
Keep a record of your learning journey. Document challenges you’ve overcome, new skills acquired, and projects you’ve contributed to. A personal learning journal can serve as a reference point for your growth and a tangible demonstration of your evolving proficiency as a programmer.
h) Network within the Organization
Build connections within your organization, networking with colleagues from different departments. It not only enriches your professional relationships but also opens doors to collaborative opportunities. A strong internal network can lead to mentorship, knowledge-sharing, and exposure to different facets of the business.
i) Pursue Further Education Opportunities
If your organization offers educational opportunities, such as workshops or courses, take advantage of them. Many companies invest in the continuous learning of their employees. Seize the chance to deepen your understanding of specific coding languages, frameworks, or development methodologies.
j) Set Clear Learning Goals
Define clear learning goals aligned with your career aspirations. Whether it’s mastering a new programming language, becoming proficient in a specific framework, or gaining expertise in a particular domain, setting goals provides direction to your on-the-job learning journey.
Remember, learning to code on the job is not just about acquiring technical skills; it’s about developing a holistic approach. A learner must focus on problem-solving, collaboration, and continuous improvement. By embracing challenges, staying curious, and actively participating in your professional development, you pave the way to becoming a proficient programmer.
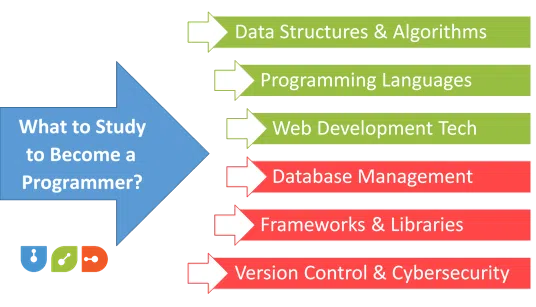
3) What to Study to Become a Programmer
Studying computer science fundamentals, algorithms, and data structures forms the core of a programmer’s education. Additionally, gaining proficiency in relevant programming languages and frameworks is crucial. Online courses, tutorials, and coding communities provide valuable resources for self-directed learning.
Studying computer science fundamentals, algorithms, and data structures forms the core of a programmer’s education. Delving into the intricacies of coding requirements, individuals aspiring to become programmers should focus on mastering the following key areas:
a) Programming Languages Proficiency
Develop a strong foundation in popular programming languages such as Python, Java, or JavaScript. Proficiency in these languages opens doors to various development opportunities and ensures compatibility with a wide range of projects.
b) Data Structures and Algorithms
Mastering data structures and algorithms is paramount for effective problem-solving and efficient code implementation. Understanding concepts like linked lists, trees, sorting algorithms, and searching algorithms equips programmers with the tools to optimize their code and tackle complex challenges.
c) Web Development Technologies
For those interested in web development, gaining expertise in relevant technologies is essential. Familiarize yourself with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for front-end development, and explore back-end technologies like Node.js or Django. Understanding web development stacks or frameworks contributes to building robust and scalable applications.
d) Database Management
Learn the basics of database management systems (DBMS) and SQL. Understanding how to design and interact with databases is crucial for storing and retrieving data efficiently. Familiarity with databases like MySQL or MongoDB enhances a programmer’s versatility.
e) Version Control
Proficiency in version control systems like Git is indispensable for collaborative coding. Version control enables tracking changes, managing collaborative projects, and reverting to previous states, ensuring a smooth and organized development process.
f) Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC)
Understanding the phases of the Software Development Lifecycle is essential. Familiarize yourself with concepts such as requirement analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. A holistic understanding of SDLC enhances a programmer’s ability to contribute to every stage of a project.
g) Frameworks and Libraries
Explore popular frameworks and libraries relevant to your chosen field. For instance, if you’re interested in front-end development, consider frameworks like React or Angular. Learning how to leverage these tools accelerates development and enhances code efficiency.
h) Cybersecurity Basics
In an era of increasing cyber threats, having a basic understanding of cybersecurity is valuable. Learn about secure coding practices, encryption, and best practices for safeguarding applications against potential vulnerabilities.
i) Soft Skills Development
While technical skills are crucial, developing soft skills is equally important. Cultivate effective communication, problem-solving, and teamwork skills. The ability to collaborate, articulate ideas, and adapt to dynamic team environments enhances a programmer’s overall effectiveness.
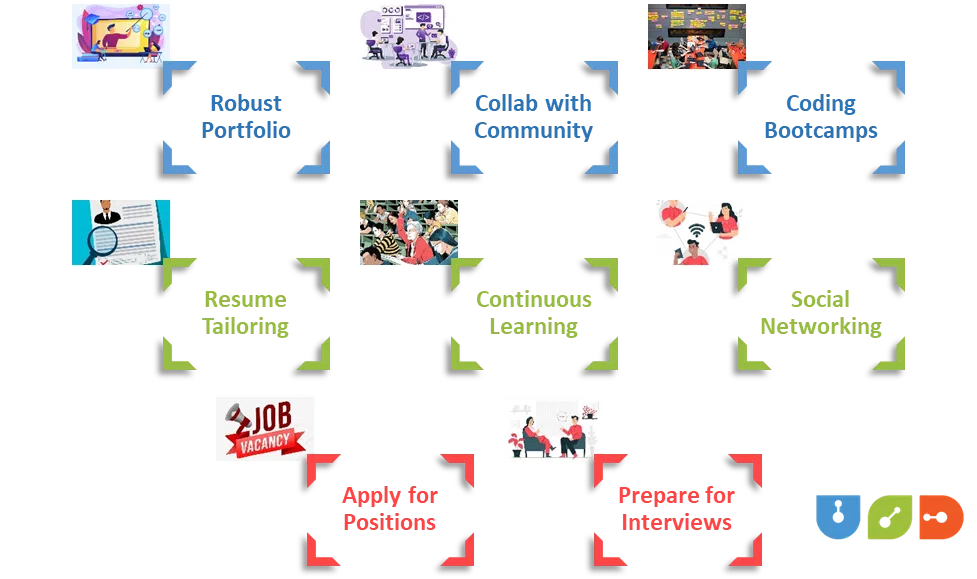
D. Learn to Code and Get a Job
Learning to code is a gateway to numerous job opportunities. Build a robust portfolio showcasing your projects, collaborate with the coding community, and actively seek job openings. Demonstrating practical skills and a passion for continuous learning make you a desirable candidate in the competitive job market.
Learning to code is not just about acquiring technical skills; it’s a strategic journey towards securing a rewarding career. Here’s a detailed exploration of the steps to learn to code effectively and transition into a successful job search.
1) Building a Robust Portfolio
Your portfolio is your digital footprint in the coding landscape. Showcase a diverse range of projects that highlight your coding proficiency. Ensure each project reflects your problem-solving abilities, creativity, and application of coding concepts. A well-curated portfolio is a powerful tool to impress potential employers.
2) Collaborate with the Coding Community
Engage with coding communities on platforms like GitHub and Stack Overflow. Actively contribute to open-source projects, participate in discussions, and seek feedback on your code. Collaborating with other developers not only enhances your coding skills but also exposes you to industry best practices and different perspectives.
3) Networking: Online and Offline
Establishing a strong professional network is a crucial aspect of job hunting. Attend virtual meetups, webinars, and conferences to connect with industry professionals. Leverage social media platforms like LinkedIn to build an online presence. Engage in discussions, share your coding journey, and follow companies of interest. Networking opens doors to hidden job opportunities and provides valuable insights into the industry.
4) Tailoring Your Resume
Craft a resume that highlights your coding experience, projects, and relevant skills. Tailor your resume to match the specific requirements of the job you’re applying for. Quantify your achievements, use action verbs, and emphasize your contributions to projects. A well-crafted resume acts as your marketing tool, making you stand out in a competitive job market.
5) Applying for Entry-Level Positions and Internships
Begin your job search by applying for entry-level positions and internships. Many companies are open to hiring individuals with potential and a strong foundation in coding. Emphasize your willingness to learn, showcase your practical experience, and express your enthusiasm for the company and role. Entry-level positions provide the hands-on experience that employers value.
6) Exploring Coding Bootcamps
Consider enrolling in coding boot camps that offer intensive, focused training. These programs often provide a structured curriculum, mentorship, and support in building a portfolio. Coding boot camps are designed to fast-track your coding skills and prepare you for the job market, making them a popular choice for career changers and beginners.
7) Continuous Learning
The world of coding is dynamic, and continuous learning is a cornerstone of success. Stay updated on the latest industry trends, coding languages, and technological advancements. Dedicate time to expand your skill set, explore new technologies, and deepen your understanding of coding concepts. A commitment to lifelong learning positions you as a valuable asset in the tech industry.
8) Navigating Interviews
Prepare for job interviews by practicing frequently asked technical questions. Understand the company’s coding practices, values, and projects before the interview. Showcase not only your technical skills but also your problem-solving approach and communication abilities. Be ready to discuss your projects, challenges you’ve overcome, and your passion for coding.

E. Conclusion
Coding is a dynamic and accessible field that welcomes individuals with diverse backgrounds. Math, while beneficial, is not a strict requirement, and aspiring programmers can acquire skills through various educational paths. Daily life as a software programmer involves a blend of coding, collaboration, and problem-solving activities. By focusing on foundational requirements and continuous learning, anyone can follow their ambitions to become a successful programmer. No matter where you start from, you can excel in this domain if you have the passion to learn.
Unique Software Development takes pride in not only developing custom solutions but also being a beacon for the developers’ community. Share your ambitions, ideas, or stories on our social media pages for community development, or contact us for your software needs. We can make necessary amendments to your custom projects, whatever stage they are at, or fine-tune them.